CO2 Emissions
At SCS Logistics BV we are very aware of the fact that the transport world with all its trucks, ships and aircraft has a major influence on the total CO2 emissions in this world. The transport sector is therefore facing an important transition. The demand for the transport of goods is still growing, but at the same time the sector is subject to increasingly strict environmental requirements.
To meet climate targets, companies must drastically reduce their emissions. Naturally, we as SCS try to do our part when it comes to reducing CO2 emissions. That is why we register and report the emissions of every transport service and every shipment. The calculation of the CO2 emissions per cargo is done according to the Glec method.
GLEC-method
The GLEC method is an abbreviation for Global Logistics Emissions Council (GLEC) Framework for Logistics Emissions Methodologies. It is a standardized methodology for calculating and reporting emissions in the logistics sector. The aim of the GLEC method is to provide a common basis for the calculation of CO2 emissions in the logistics sector, so that reliable and comparable data are available.
The GLEC method is supported by several organizations, such as the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the Smart Freight Centre. By using the GLEC method, companies can accurately calculate greenhouse gas emissions in their supply chain and then take targeted measures to reduce these emissions. This can contribute to reducing the impact of the logistics sector on the environment and the fight against climate change.
Calculation
To calculate how much a vehicle emits, we need a number of data. Loading address, unloading address, the type of car, the loading meters and the weight of the shipment. Based on this information, the emissions of a shipment are automatically calculated by our system.
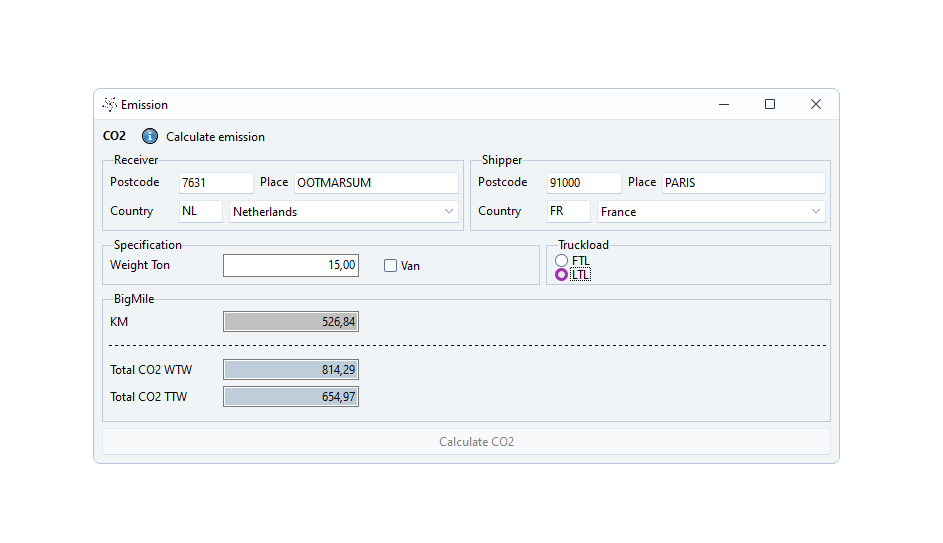
* WTW stands for ‘Well to Wheel’. This means that the WTW emissions take into account both the emissions released during combustion in the engine, for example, and the production process.
* TTW stands for ‘Tank to Wheel’. This means that only the emissions that the vehicle itself emits are calculated here.